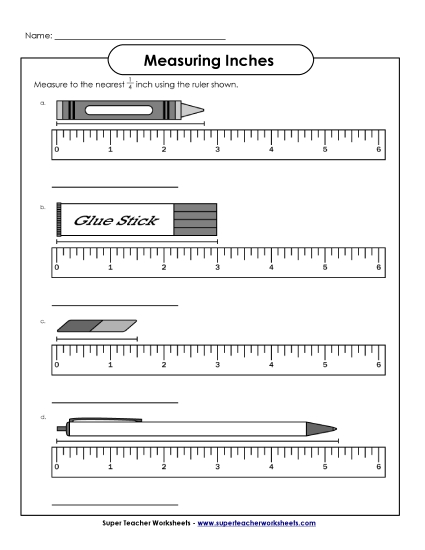
2.MD.1:
Measurement And Data
Measure And Estimate Lengths In Standard Units.
Measure the length of an object by selecting and using appropriate tools such as rulers, yardsticks, meter sticks, and measuring tapes.
1.MD.2:
Measurement And Data
Measure Lengths Indirectly And By Iterating Length Units.
Express the length of an object as a whole number of length units, by laying multiple copies of a shorter object (the length unit) end to end; understand that the length measurement of an object is the number of same-size length units that span it with no gaps or overlaps. Limit to contexts where the object being measured is spanned by a whole number of length units with no gaps or overlaps.
3.MD.2:
Measurement And Data
Solve Problems Involving Measurement And Estimation Of Intervals Of Time, Liquid Volumes, And Masses Of Objects.
Measure and estimate liquid volumes and masses of objects using standard units of grams (g), kilograms (kg), and liters (l).6 Add, subtract, multiply, or divide to solve one-step word problems involving masses or volumes that are given in the same units, e.g., by using drawings (such as a beaker with a measurement scale) to represent the problem.7
4.MD.2:
Measurement And Data
Solve Problems Involving Measurement And Conversion Of Measurements From A Larger Unit To A Smaller Unit.
Use the four operations to solve word problems involving distances, intervals of time, liquid volumes, masses of objects, and money, including problems involving simple fractions or decimals, and problems that require expressing measurements given in a larger unit in terms of a smaller unit. Represent measurement quantities using diagrams such as number line diagrams that feature a measurement scale.