3.MD.8:
Measurement And Data
Geometric Measurement: Recognize Perimeter As An Attribute Of Plane Figures And Distinguish Between Linear And Area Measures.
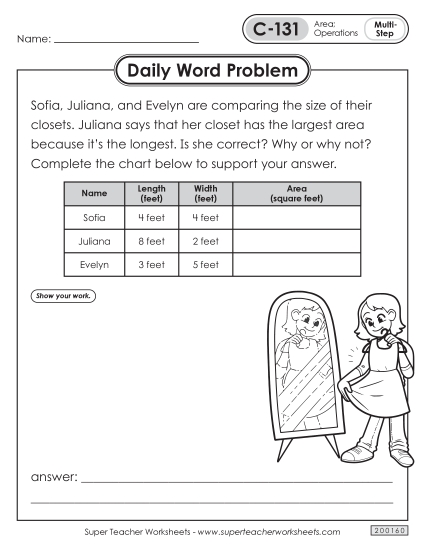
Solve real world and mathematical problems involving perimeters of polygons, including finding the perimeter given the side lengths, finding an unknown side length, and exhibiting rectangles with the same perimeter and different areas or with the same area and different perimeters.
3.MD.7:
Measurement And Data
Geometric Measurement: Understand Concepts Of Area And Relate Area To Multiplication And To Addition.
Relate area to the operations of multiplication and addition.
3.MD.7b:
Measurement And Data
Geometric Measurement: Understand Concepts Of Area And Relate Area To Multiplication And To Addition.
Multiply side lengths to find areas of rectangles with whole- number side lengths in the context of solving real world and mathematical problems, and represent whole-number products as rectangular areas in mathematical reasoning.
3.MD.1:
Measurement And Data
Solve Problems Involving Measurement And Estimation Of Intervals Of Time, Liquid Volumes, And Masses Of Objects.
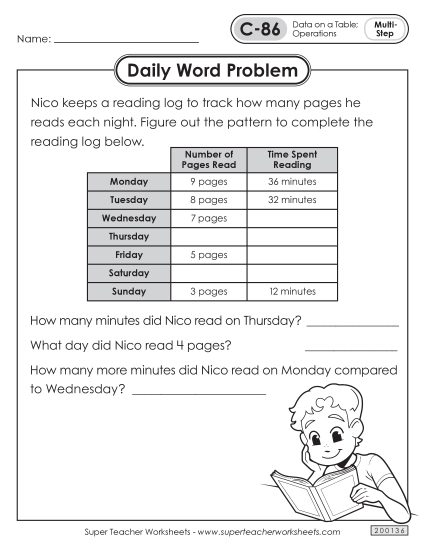
Tell and write time to the nearest minute and measure time intervals in minutes. Solve word problems involving addition and subtraction of time intervals in minutes, e.g., by representing the problem on a number line diagram.
3.NF.3b:
Number And Operations - Fractions
Develop Understanding Of Fractions As Numbers.
Recognize and generate simple equivalent fractions, e.g., 1/2 = 2/4, 4/6 = 2/3). Explain why the fractions are equivalent, e.g., by using a visual fraction model.
3.NF.3d:
Number And Operations - Fractions
Develop Understanding Of Fractions As Numbers.
Compare two fractions with the same numerator or the same denominator by reasoning about their size. Recognize that comparisons are valid only when the two fractions refer to the same whole. Record the results of comparisons with the symbols >, =, or <, and justify the conclusions, e.g., by using a visual fraction model.
3.NBT.2:
Number And Operations In Base Ten
Use Place Value Understanding And Properties Of Operations To Perform Multi-Digit Arithmetic
Fluently add and subtract within 1000 using strategies and algorithms based on place value, properties of operations, and-or the relationship between addition and subtraction.
3.OA.7:
Operations And Algebraic Thinking
Multiply And Divide Within 100.
Fluently multiply and divide within 100, using strategies such as the relationship between multiplication and division (e.g., knowing that 8 x 5 = 40, one knows 40 / 5 = 8) or properties of operations. By the end of Grade 3, know from memory all products of two one-digit numbers.
3.OA.8:
Operations And Algebraic Thinking
Solve Problems Involving The Four Operations, And Identify And Explain Patterns In Arithmetic.
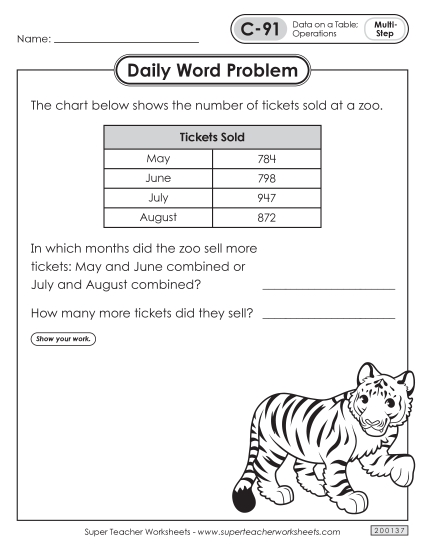
Solve two-step word problems using the four operations. Represent these problems using equations with a letter standing for the unknown quantity. Assess the reasonableness of answers using mental computation and estimation strategies including rounding.3