4.NBT.5:
Number And Operations In Base Ten
Use Place Value Understanding And Properties Of Operations To Perform Multi-Digit Arithmetic.
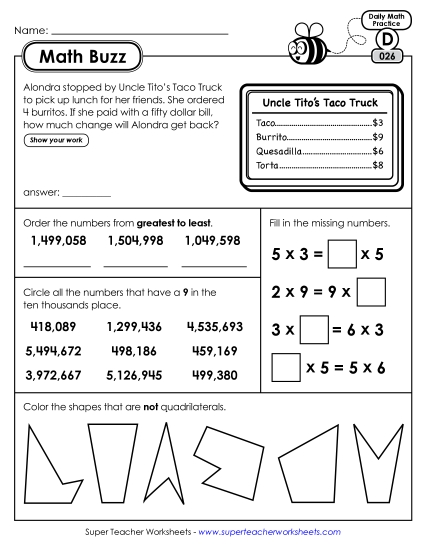
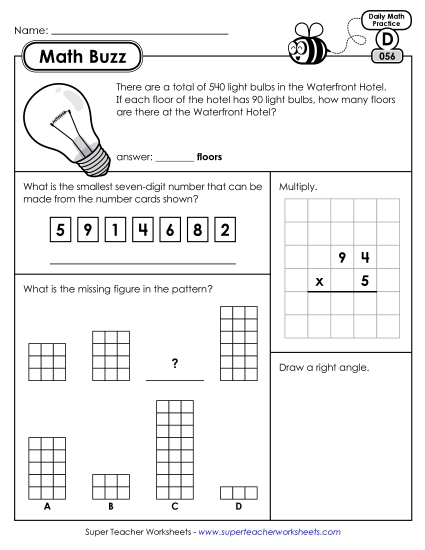
Multiply a whole number of up to four digits by a one-digit whole number, and multiply two two-digit numbers, using strategies based on place value and the properties of operations. Illustrate and explain the calculation by using equations, rectangular arrays, and/or area models.
4.NF.1:
Number And Operations - Fractions
Extend Understanding Of Fraction Equivalence And Ordering.
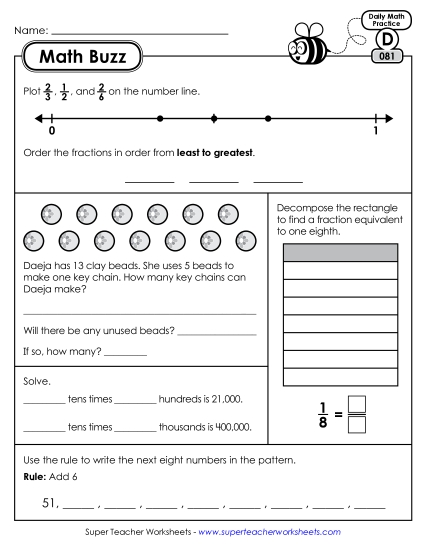
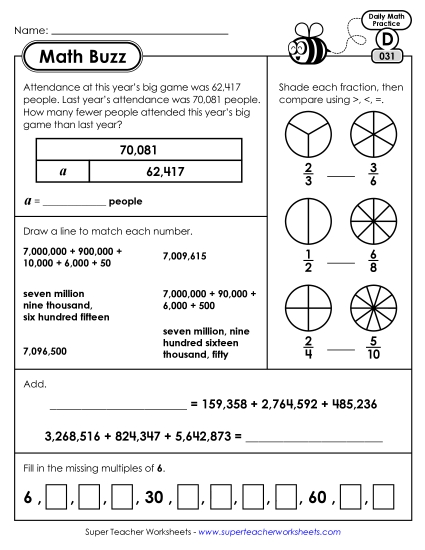
Explain why a fraction a/b is equivalent to a fraction (n x a)/(n x b) by using visual fraction models, with attention to how the number and size of the parts differ even though the two fractions themselves are the same size. Use this principle to recognize and generate equivalent fractions.
4.MD.3:
Measurement And Data
Solve Problems Involving Measurement And Conversion Of Measurements From A Larger Unit To A Smaller Unit.
Apply the area and perimeter formulas for rectangles in real world and mathematical problems. For example, find the width of a rectangular room given the area of the flooring and the length, by viewing the area formula as a multiplication equation with an unknown factor.
4.OA.3:
Operations And Algebraic Thinking
Use The Four Operations With Whole Numbers To Solve Problems.
Solve multistep word problems posed with whole numbers and having whole-number answers using the four operations, including problems in which remainders must be interpreted. Represent these problems using equations with a letter standing for the unknown quantity. Assess the reasonableness of answers using mental computation and estimation strategies including rounding.