2.NBT.2:
Number And Operations In Base Ten
Understand Place Value.
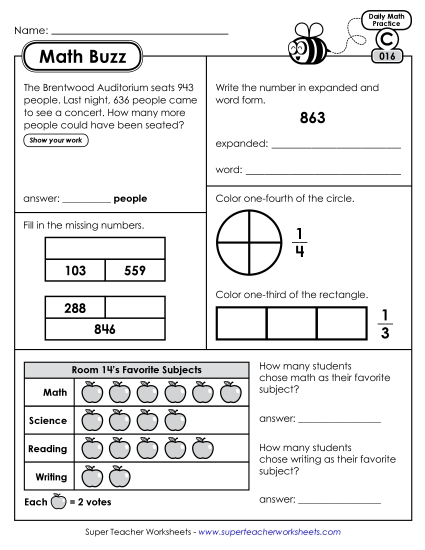
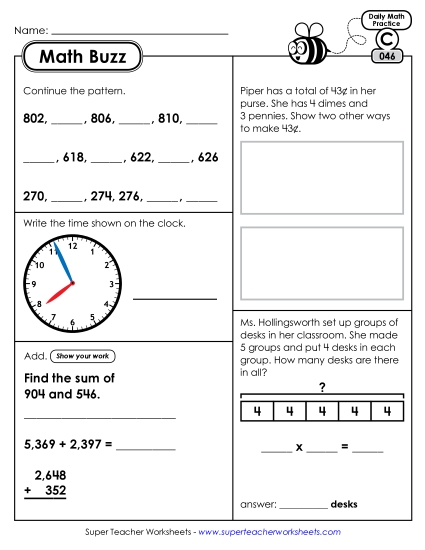
Count within 1000; skip-count by 5s, 10s, and 100s.
2.NBT.5:
Number And Operations In Base Ten
Use Place Value Understanding And Properties Of Operations To Add And Subtract.
Fluently add and subtract within 100 using strategies based on place value, properties of operations, and/or the relationship between addition and subtraction.
2.NBT.7:
Number And Operations In Base Ten
Use Place Value Understanding And Properties Of Operations To Add And Subtract.
Add and subtract within 1000, using concrete models or drawings and strategies based on place value, properties of operations, and/or the relationship between addition and subtraction; relate the strategy to a written method. Understand that in adding or subtracting three- digit numbers, one adds or subtracts hundreds and hundreds, tens and tens, ones and ones; and sometimes it is necessary to compose or decompose tens or hundreds.
3.NBT.2:
Number And Operations In Base Ten
Use Place Value Understanding And Properties Of Operations To Perform Multi-Digit Arithmetic
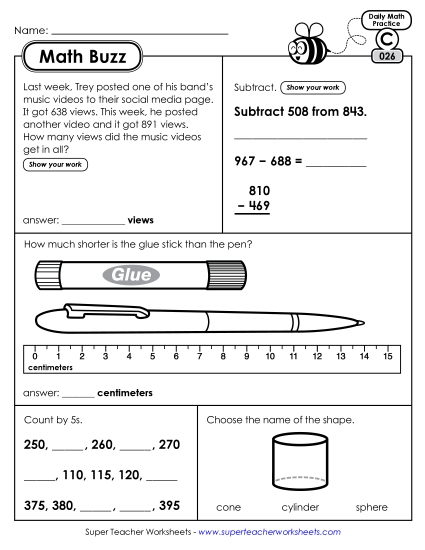
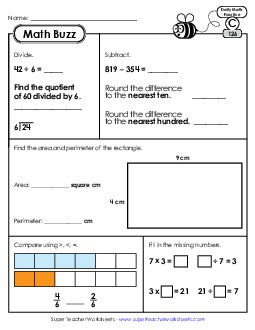
Fluently add and subtract within 1000 using strategies and algorithms based on place value, properties of operations, and-or the relationship between addition and subtraction.
2.MD.8:
Measurement And Data
Work With Time And Money.
Solve word problems involving dollar bills, quarters, dimes, nickels, and pennies, using $ and c symbols appropriately. Example: If you have 2 dimes and 3 pennies, how many cents do you have?
2.MD.7:
Measurement And Data
Work With Time And Money.
Tell and write time from analog and digital clocks to the nearest five minutes, using a.m. and p.m.
2.OA.1:
Operations And Algebraic Thinking
Represent And Solve Problems Involving Addition And Subtraction.
Use addition and subtraction within 100 to solve one- and two-step word problems involving situations of adding to, taking from, putting together, taking apart, and comparing, with unknowns in all positions, e.g., by using drawings and equations with a symbol for the unknown number to represent the problem.1
2.G.1:
Geometry
Reason With Shapes And Their Attributes.
Recognize and draw shapes having specified attributes, such as a given number of angles or a given number of equal faces.5 Identify triangles, quadrilaterals, pentagons, hexagons, and cubes.
2.MD.2:
Measurement And Data
Measure And Estimate Lengths In Standard Units.
Measure the length of an object twice, using length units of different lengths for the two measurements; describe how the two measurements relate to the size of the unit chosen.
2.NBT.6:
Number And Operations In Base Ten
Use Place Value Understanding And Properties Of Operations To Add And Subtract.
Add up to four two-digit numbers using strategies based on place value and properties of operations.
2.MD.3:
Measurement And Data
Measure And Estimate Lengths In Standard Units.
Estimate lengths using units of inches, feet, centimeters, and meters.
2.MD.10:
Measurement And Data
Represent And Interpret Data.
Draw a picture graph and a bar graph (with single-unit scale) to represent a data set with up to four categories. Solve simple put- together, take-apart, and compare problems4 using information presented in a bar graph.
2.MD.5:
Measurement And Data
Relate Addition And Subtraction To Length.
Use addition and subtraction within 100 to solve word problems involving lengths that are given in the same units, e.g., by using drawings (such as drawings of rulers) and equations with a symbol for the unknown number to represent the problem.