4.NBT.6:
Number And Operations In Base Ten
Use Place Value Understanding And Properties Of Operations To Perform Multi-Digit Arithmetic.
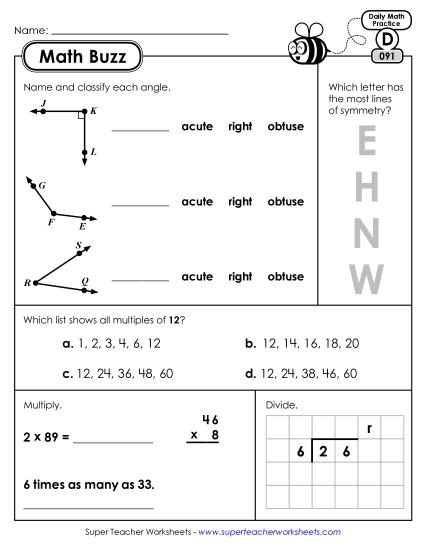
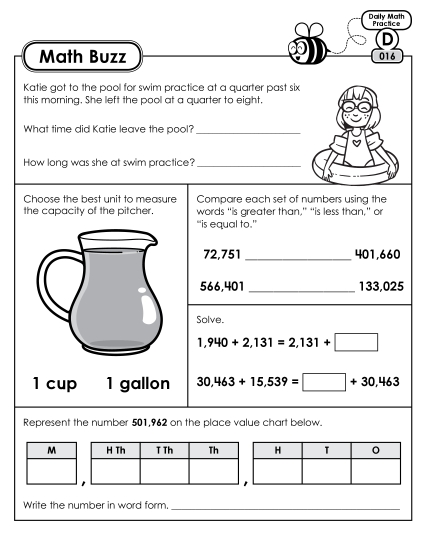
Find whole-number quotients and remainders with up to four-digit dividends and one-digit divisors, using strategies based on place value, the properties of operations, and/or the relationship between multiplication and division. Illustrate and explain the calculation by using equations, rectangular arrays, and/or area models.
4.G.1:
Geometry
Draw And Identify Lines And Angles, And Classify Shapes By Properties Of Their Lines And Angles.
Draw points, lines, line segments, rays, angles (right, acute, obtuse), and perpendicular and parallel lines. Identify these in two-dimensional figures.
4.NF.2:
Number And Operations - Fractions
Extend Understanding Of Fraction Equivalence And Ordering.
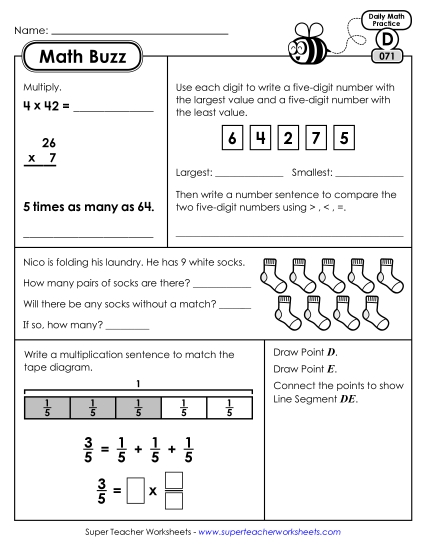
Compare two fractions with different numerators and different denominators, e.g., by creating common denominators or numerators, or by comparing to a benchmark fraction such as 1/2. Recognize that comparisons are valid only when the two fractions refer to the same whole. Record the results of comparisons with symbols >, =, or <, and justify the conclusions, e.g., by using a visual fraction model.
4.OA.5:
Operations And Algebraic Thinking
Generate And Analyze Patterns.
Generate a number or shape pattern that follows a given rule. Identify apparent features of the pattern that were not explicit in the rule itself. For example, given the rule "Add 3" and the starting number 1, generate terms in the resulting sequence and observe that the terms appear to alternate between odd and even numbers. Explain informally why the numbers will continue to alternate in this way.