2.G.2:
Geometry
Reason With Shapes And Their Attributes.
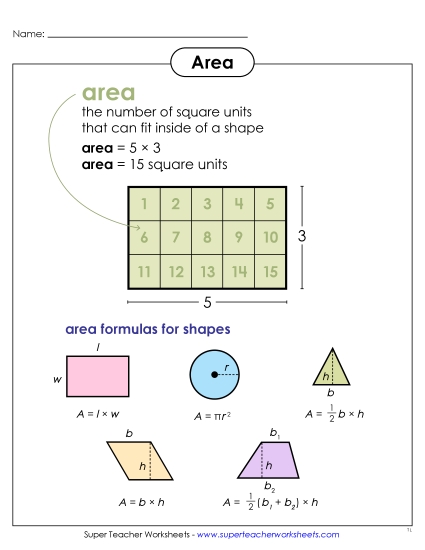
Partition a rectangle into rows and columns of same-size squares and count to find the total number of them.
3.G.2:
Geometry
Reason With Shapes And Their Attributes.
Partition shapes into parts with equal areas. Express the area of each part as a unit fraction of the whole. For example, partition a shape into 4 parts with equal area, and describe the area of each part as 1/4 of the area of the shape.
3.MD.5:
Measurement And Data
Geometric Measurement: Understand Concepts Of Area And Relate Area To Multiplication And To Addition.
Recognize area as an attribute of plane figures and understand concepts of area measurement.
3.MD.6:
Measurement And Data
Geometric Measurement: Understand Concepts Of Area And Relate Area To Multiplication And To Addition.
Measure areas by counting unit squares (square cm, square m, square in, square ft, and improvised units).
3.MD.7a:
Measurement And Data
Geometric Measurement: Understand Concepts Of Area And Relate Area To Multiplication And To Addition.
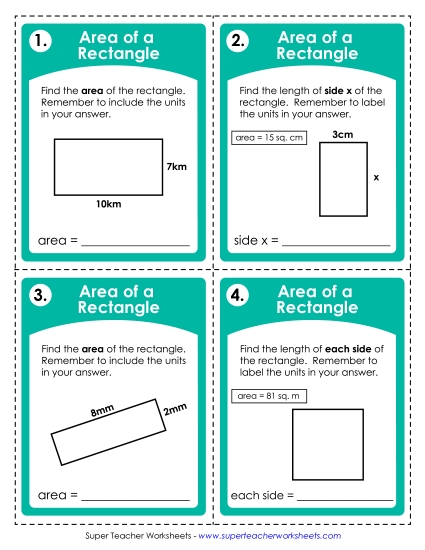
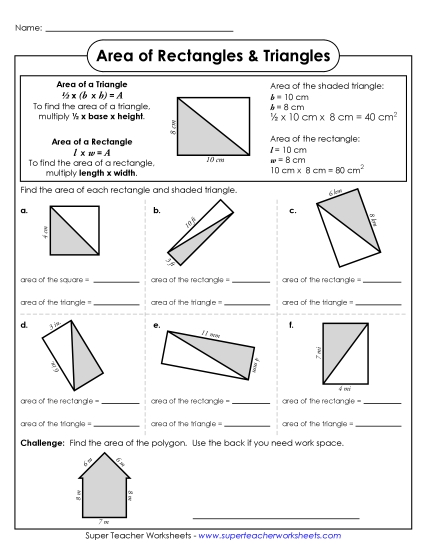
Find the area of a rectangle with whole-number side lengths by tiling it, and show that the area is the same as would be found by multiplying the side lengths.
3.MD.7b:
Measurement And Data
Geometric Measurement: Understand Concepts Of Area And Relate Area To Multiplication And To Addition.
Multiply side lengths to find areas of rectangles with whole- number side lengths in the context of solving real world and mathematical problems, and represent whole-number products as rectangular areas in mathematical reasoning.